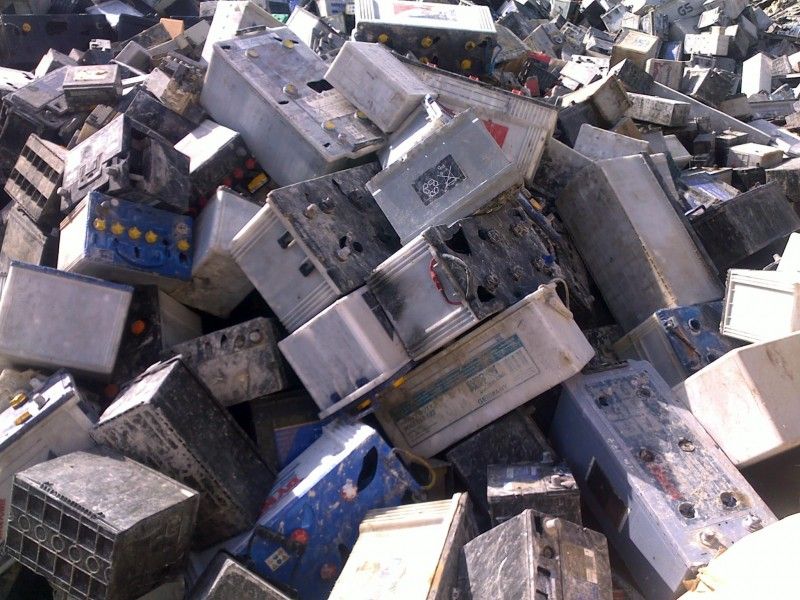
Trading lead battery scraps, when managed responsibly, can have positive effects on the environment. The recycling and reclamation of lead from battery scraps contributes to the sustainable management of resources, reducing the environmental impacts associated with lead mining and primary lead production. This article delves into the positive effects of trading lead battery scraps on the environment, emphasizing the opportunities for resource conservation, emissions reduction, and circular economy principles.
The global trade of lead battery scraps plays a pivotal role in the circular economy, fostering resource conservation and sustainable practices within the lead industry. Lead-acid batteries, utilized in a multitude of applications such as automotive vehicles, industrial machinery, and energy storage systems, contribute to the generation of battery scraps. These scraps, rich in lead and sulfuric acid, provide an invaluable input for lead recycling, thereby mitigating the environmental impacts of primary lead production.
Furthermore, trading lead battery scraps promotes the efficient utilization of secondary raw materials, reducing the reliance on primary lead production and the associated environmental impacts. By integrating battery scrap trading into the lead recycling supply chain, companies and industries involved in lead recycling can harness the inherent environmental benefits of reusing and reclaiming lead from discarded batteries.
In addition to reducing the demand for primary lead production, trading lead battery scraps supports the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The recycling of lead from battery scraps requires significantly less energy compared to primary lead production, leading to a reduction in carbon emissions and the overall environmental footprint of lead production.
Moreover, responsible trading practices uphold the principles of sustainable waste management, ensuring that lead battery scraps are handled, transported, and processed in an environmentally sound manner. Stringent environmental regulations and industry best practices guide the responsible trading and recycling of lead battery scraps, minimizing the release of lead and sulfuric acid into the environment, and mitigating the associated environmental risks.
The positive environmental effects of trading lead battery scraps extend to the conservation of natural resources, reduction of mining activities, and the protection of ecosystems. Moreover, the circular flow of lead through trading and recycling processes embodies the essence of a sustainable, environmentally conscious approach to resource management.
In conclusion, the trading of lead battery scraps presents a promising avenue for advancing environmental sustainability within the lead industry. By prioritizing responsible waste management, efficient recycling processes, and the circular economy principles, the trading of lead battery scraps stands as an opportunity to minimize the environmental impacts of lead production, conserve resources, and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable future.